Conduit fittings play a crucial role in ensuring the safety and efficiency of electrical systems in hazardous locations. Understanding the different types of conduit fittings and their functions is essential for maintaining a secure environment. Additionally, being aware of the classification of hazardous locations and the common hazards associated with them helps in identifying potential risks.
Understanding Conduit Fittings
Conduit fittings are essential components in electrical systems that connect and protect electrical wiring conductors. They provide a reliable pathway for cables and wires while ensuring proper grounding and protection against environmental factors.
When it comes to electrical installations, attention to detail is crucial. Conduit fittings play a vital role in ensuring the safety and efficiency of the entire system. Let’s dive deeper into the world of cable conduit fittings and explore the different types available.
Types of Conduit Fittings
One commonly used type of conduit fitting is the threaded connector. Threaded connectors are widely used in hazardous locations where there is a need for secure connections. These fittings have a male-threaded end to attach to the female-threaded opening of junction boxes or enclosures.
For environments that demand extra protection against moisture and contaminants, compression fittings are the go-to choice. These fittings create a tight seal by compressing a ring or ferrule over the conduit, ensuring a reliable barrier against the elements. They are particularly popular in wet and corrosive environments, where the integrity of the electrical system is of utmost importance.
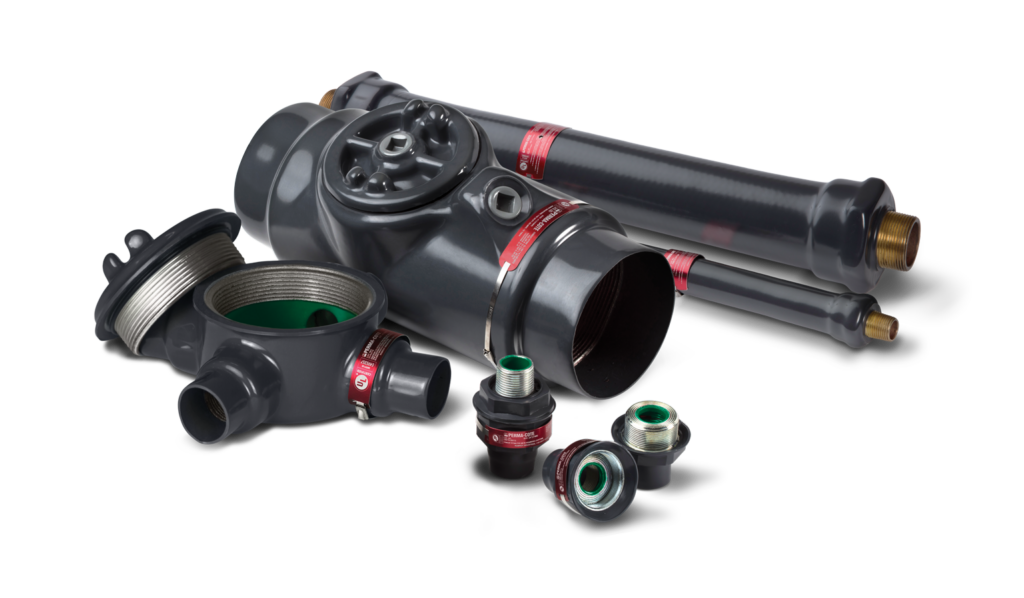

Additionally, there are also push-fit fittings that offer a quick and easy installation process. These fittings have a mechanical locking mechanism that securely holds the conduit in place without the need for any additional tools. This innovative design not only saves time but also ensures a secure connection, making them a favorite among electricians.
See Also: Safety Tips for Properly Handling and Storing Electrical Supplies
Role of Conduit Fittings in Electrical Systems
Conduit fittings serve multiple important functions in electrical systems. Firstly, they protect the wiring conductors from damage and exposure to hazardous elements. By providing a secure enclosure, conduit fittings prevent physical damage, such as impact or crushing, which can lead to electrical shorts or accidents.
Moreover, conduit fittings ensure the grounding of electrical systems, reducing the risk of electric shocks and fires. They create a continuous path for fault currents, allowing them to safely dissipate into the ground. This crucial safety feature provides peace of mind to both homeowners and professionals working with electrical installations.
Conduit fittings also aid in the organization and management of cables and wires, preventing tangling and promoting a clean and efficient installation. With the help of various fittings, electricians can neatly route and secure the wiring, ensuring easy access for maintenance and troubleshooting.
Furthermore, conduit fittings contribute to the overall longevity and reliability of electrical systems. By protecting the wiring conductors from external factors such as moisture, dust, and chemicals, these fittings help extend the lifespan of the system, reducing the need for frequent repairs or replacements.
In conclusion, conduit fittings are not just mere accessories in electrical systems. They are the unsung heroes that provide protection, organization, and efficiency. Whether it’s the threaded connectors, compression fittings, or push-fit fittings, each type has its unique purpose and benefits. So, the next time you encounter conduit fittings, remember their crucial role in keeping our electrical systems safe and reliable.
Identifying Hazardous Locations
Knowing and understanding hazardous locations is crucial for implementing the appropriate safety measures and selecting suitable conduit fittings. By identifying these locations, potential risks can be mitigated, ensuring the safety of personnel and equipment.
When it comes to hazardous locations, classifications play a significant role in determining the level of danger and the necessary safety precautions. These classifications are based on the presence of flammable gases, vapors, combustible dusts, or ignitable fibers.
Classification of Hazardous Locations
Hazardous locations in North America are categorized using classes and divisions, while international standards like the IECEx system use zones. Understanding these classifications is essential for effectively managing the risks associated with each type of hazardous location.
Class I hazardous locations involve flammable gases or vapors, such as gasoline or propane. These locations require special attention due to the potential for explosive atmospheres. Class II locations, on the other hand, deal with combustible dusts. Industries such as flour mills or coal mines fall under this classification. Lastly, Class III locations are defined by the presence of ignitable fibers, such as textiles or wood shavings, which can pose a fire hazard.
Divisions further specify the level of hazard within each class. Division 1 refers to a location where flammable substances are continuously present, requiring constant vigilance and strict safety measures. Division 2, on the other hand, indicates that the presence of flammable substances is only expected under abnormal conditions, allowing for a slightly lower level of precaution.
In contrast, the international classification system uses zones to categorize hazardous locations. Zone 0 represents an area where explosive atmospheres are present continuously or for long periods. These areas require the highest level of safety measures and precautions. Zone 1 signifies the presence of explosive atmospheres during normal operation, while Zone 2 represents the possibility of explosive atmospheres only during abnormal conditions.
Common Hazards in These Locations
Identifying hazardous locations is just the first step in ensuring safety. Understanding the common hazards associated with these locations is equally important in implementing effective safety measures.
In Class I and Zone 0 or 1 locations, the risk of sparks and arc flashes is high due to the presence of flammable gases or vapors. Electrical equipment in these areas must be carefully designed and manufactured to prevent any potential ignition sources. Special explosion-proof or intrinsically safe devices are often used to minimize the risk of explosions or fires.
Class II and Zone 20 or 21 locations pose a different set of hazards. The accumulation of combustible dust can lead to explosive atmospheres when ignited. Industries such as grain handling facilities or pharmaceutical manufacturing plants need to implement proper dust control measures and use equipment specifically designed to prevent dust ignition.
In Class III and Zone 22 locations, the presence of ignitable fibers increases the risk of fires and the spread of flames. Industries such as textile mills or woodworking shops need to ensure that their electrical equipment is adequately protected against potential ignition sources.
By understanding the common hazards in each type of hazardous location, appropriate safety measures can be implemented. This includes proper equipment selection, regular maintenance, and employee training to minimize the risk of accidents and ensure the safety of all personnel.
Electrical equipment installed in hazardous locations must be designed and manufactured to prevent the ignition of flammable substances. This is often achieved through the use of explosion-proof or intrinsically safe devices. These devices are specifically engineered to contain any potential sparks or heat, preventing them from igniting the surrounding flammable atmosphere.
In conclusion, identifying hazardous locations and understanding their classifications and common hazards is crucial for maintaining a safe working environment. By implementing the appropriate safety measures and selecting suitable equipment, the risks associated with these locations can be effectively managed, ensuring the well-being of personnel and the protection of valuable assets.

Safety Standards for Conduit Fittings
National and International Safety Standards
Several safety standards have been established to ensure the proper design, installation, and use of conduit fittings in hazardous locations.
In North America, organizations like the National Electrical Code (NEC) provide guidelines for safe electrical installations. The NEC includes specific requirements for conduit fittings used in hazardous locations to minimize the risk of explosions or fires.
Internationally, organizations like the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) define safety standards for conduit fittings and electrical systems in hazardous areas. These standards help harmonize safety practices worldwide.
Importance of Compliance with Safety Standards
Compliance with safety standards is essential to ensure the safety and integrity of electrical systems in hazardous locations.
Adhering to safety standards helps minimize the risks associated with explosions, fires, and electrical malfunctions. It ensures that conduit fittings are designed, tested, and verified to withstand the harsh conditions of hazardous locations.
Using non-compliant conduit fittings can pose severe risks, compromising the safety of both personnel and equipment. It is crucial to prioritize safety and select fittings that meet the required safety standards.
Selection of Conduit Fittings for Hazardous Locations
Factors to Consider in Selection
Choosing the right conduit fittings for hazardous locations requires careful consideration of various factors.
The type of hazardous location, as classified by the NEC or international standards, plays a significant role in determining the suitability of conduit fittings. Different locations have different requirements for ingress protection, temperature ratings, and resistance to chemicals or corrosive substances.
The materials used in the construction of conduit fittings are also essential. Non-corrosive and explosion-proof materials such as stainless steel or brass are commonly recommended for hazardous locations.
Material and Design Considerations
As mentioned earlier, the material used in conduit fittings is critical for their effectiveness in hazardous locations.
Stainless steel fittings are known for their corrosion resistance and durability, making them suitable for environments with high moisture or chemical exposure. Brass fittings are also commonly used due to their strength and resistance to corrosion.
Additionally, the design of conduit fittings should consider the ease of installation and maintenance. Fittings with innovative features like self-locking mechanisms or quick-connect systems can streamline the installation process and reduce the risk of errors.
Installation and Maintenance of Conduit Fittings
Safe Installation Practices
Proper installation practices are crucial to ensure the safe and reliable operation of conduit fittings in hazardous locations.
Firstly, it is crucial to follow the manufacturer’s instructions and guidelines during installation. These instructions provide specific details and precautions for the particular conduit fittings being used.
The use of appropriate tools and equipment is essential to prevent damage to the fittings or the electrical wiring. Proper training should be provided to installers to ensure they are familiar with the correct installation procedures.
Furthermore, regular inspections during and after installation are necessary to identify any issues or defects that could compromise the effectiveness of the fittings.
Regular Maintenance and Inspection
Ongoing maintenance and inspection are essential to ensure the continued safety and performance of conduit fittings in hazardous locations.
Regular inspections should include checks for signs of damage, such as cracks, corrosion, or loose connections. Any damaged or worn-out fittings should be immediately replaced to prevent potential hazards.
Additionally, maintaining a clean and organized environment around conduit fittings helps prevent the accumulation of dust or debris, reducing the risk of issues such as overheating or short circuits.
Periodic testing and verification of conduit fittings, as recommended by the safety standards, can provide assurance of their continued effectiveness in hazardous environments.In conclusion, conduit fittings play a vital role in ensuring the safety and efficiency of electrical systems in hazardous locations. Understanding the different types of fittings, the classification of hazardous locations, and the importance of safety standards aids in making informed decisions about their selection and installation. Regular maintenance and inspections help ensure the continued protection provided by conduit fittings, promoting a secure environment for personnel and equipment in hazardous locations.
